Global Cooling Innovations
We need innovative cooling technologies
Cooling is a global necessity
Cooling — both air conditioning and refrigeration — is no longer a luxury but a global necessity, essential for human productivity, health, and survival. Over half of the global population now faces deadly heat conditions, of which a third have little to no access to cooling solutions.
This creates a fundamental dilemma: balancing comfortable living conditions with the urgent need to reduce carbon emissions.
Yet, scaling cooling sustainably will require innovation that reduces emissions while expanding equitable access.

Leapfrog Potential
Carbon emissions from cooling are significant and growing rapidly. Refrigeration and space cooling are responsible for over 10 percent of global climate pollution, or 4.4 GtCO2e annually, with an additional 1 GtCO2e from food loss due to inadequate refrigeration.
Cooling-related emissions are expected to double by 2050, driven by increasing temperatures and a growing middle class. Beyond emissions, cooling is expected to drive peak electricity demand, especially in hot countries, putting additional strain on already stressed grids and potentially requiring new power plants to meet demand.
We need to expand the use of best-available efficient technologies today while investing in next-generation solutions—such as solid-state and passive radiative cooling—that show strong potential to improve efficiency, access, and resilience.
These revolutionary technologies represent a huge leapfrog potential — they can offer step-change improvement in performance and will be maturing (and getting affordable enough) just as demand for ACs starts to take off in many parts of Asia and Africa.
Key Innovation Areas
Solid-State Cooling
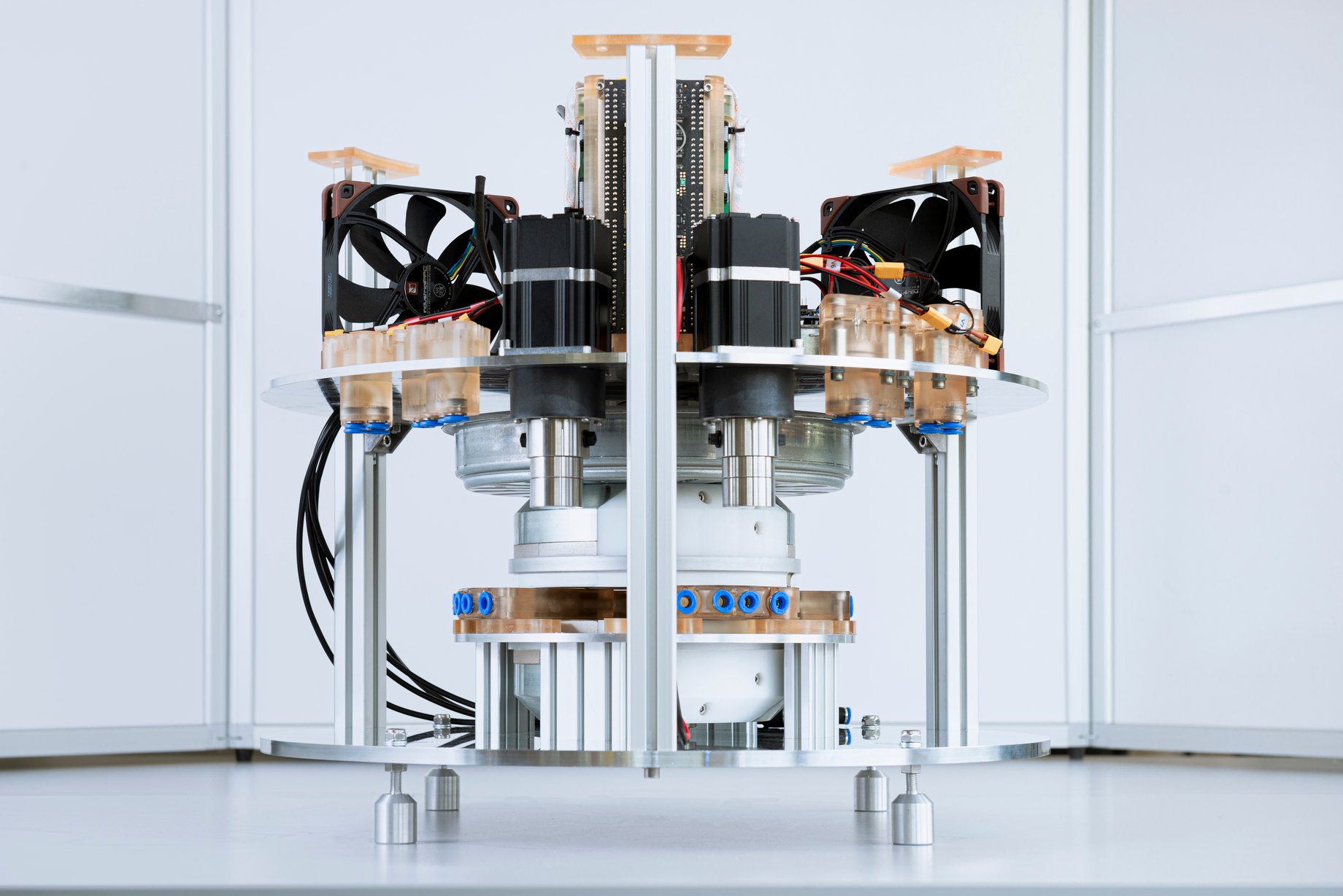
The core principle of solid-state cooling systems is the caloric effect, which means that a solid material can change temperature by applying an external force or field. These systems use solid-state chips or advanced materials to provide efficient, refrigerant-free space cooling.
Passive Daytime Radiative Cooling
Passive daytime radiative cooling solutions reflect sunlight and remove building heat by radiating it at mid-infrared wavelengths designed to pass directly through the atmosphere and into deep space. Examples include paints, films, and membranes that passively cool surfaces without energy use.
Super-Efficient Cooling
A new wave of ultra-efficient cooling technologies is transforming how we keep our homes, businesses, and supply chains cool. By combining cutting-edge efficiency with refrigerants that have little to no climate impact, these systems deliver powerful cooling with a fraction of today’s energy use, helping decarbonize one of the world’s fastest-growing energy demands.
Partner With Us to Advance Passive Daytime Radiative Cooling
Third Derivative and RMI are working to validate the performance of passive daytime radiative cooling (PDRC) materials in diverse climates and building types to accelerate commercialization in the United States and India. These pilots are designed to collect data, validate performance, and explore equitable pathways for deployment in both heat-vulnerable communities and commercial contexts.

RMI's Global Cooling Initiative
RMI has deep expertise across heat resilience, sustainable cooling, and buildings. We're working to accelerate sustainable cooling solutions by advancing energy-efficient technologies, eco-friendly refrigerants, and improved refrigerant management.























.png)